Intro
In the previous posts we go over how to build docker images, and how to create and manage permissions over Kubernetes users, now we are going to see how we can use those things to deploy automatically to a cluster using code build.
Before continue with the configuration we need to find the right place to store the token that we are going to use access the cluster, that place is the Secret Manager in AWS.
Configuring Secret Manager
When we create the buildspec.yml (link) one of the steps was to create a
Role, that role is used to execute the buildspec.yml, in order to access Secret Manager
additional permissions are required, so go to “Services”, search for “IAM” and click on it.
Click on Roles and search for the role created in AWS Code Build
Click on “Attach policies” and then on “Create Policy” as shown on the image below
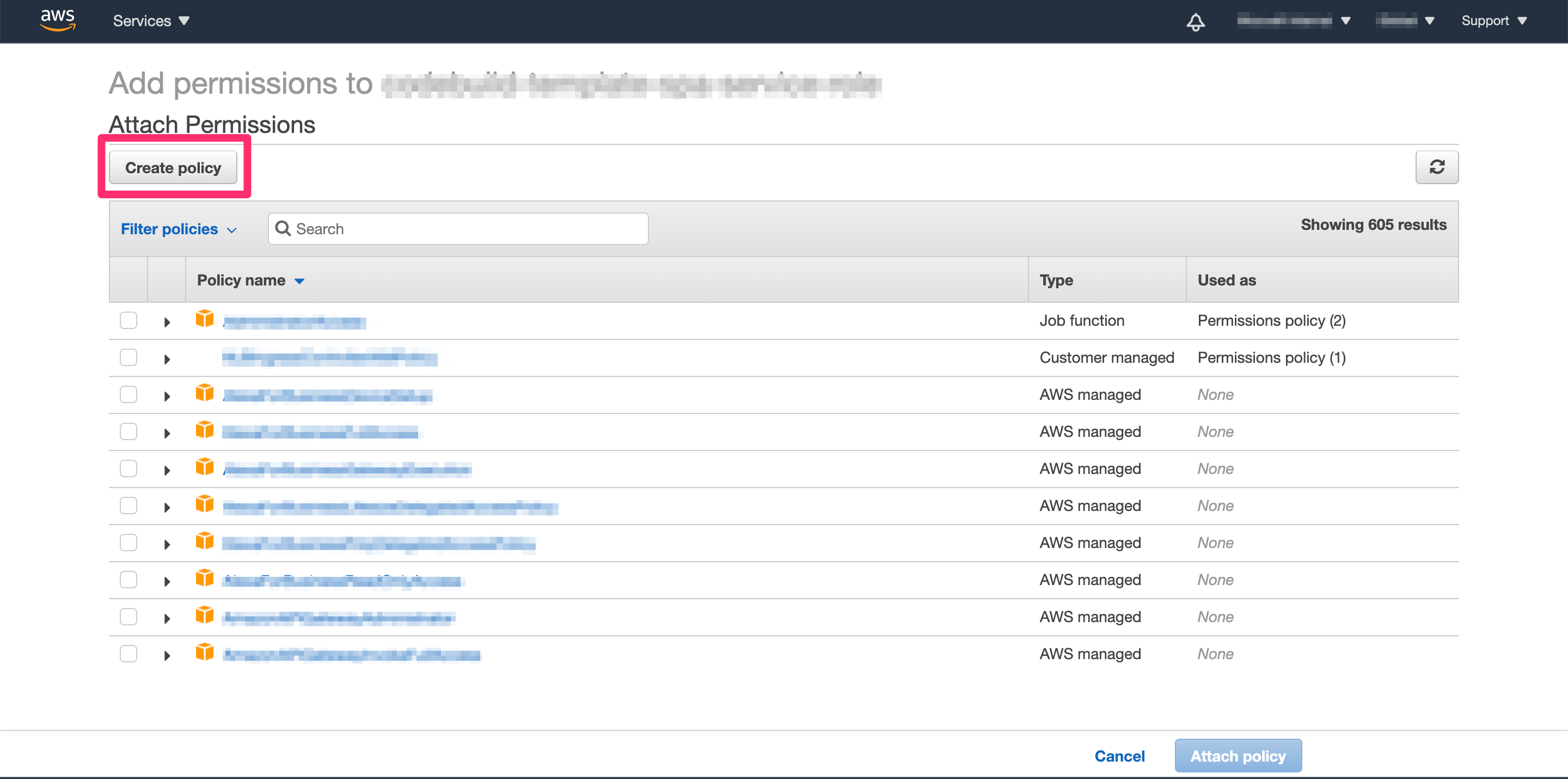
From there click on “JSON” and paste the following policy (if you need more security just restrict the resources for that policy to the once that you want to give access to, but in this example we are going to give access to all resources)
1{2 "Version": "2012-10-17",3 "Statement": {4 "Effect": "Allow",5 "Action": [6 "secretsmanager:Describe*",7 "secretsmanager:Get*",8 "secretsmanager:List*"9 ],10 "Resource": "*"11 }12}
Name that policy FullReadSecretsManager and create it.
Once created you need to attach that policy to the existing Role go back to roles and search
for the one previously created. Click on Attach Policy and search for FullReadSecretsManager
click on the checkbox near to the policy and click on button that says “Attach Policy”
Code Build script (buildspec.yml)
Now we are going to add additional steps to our code build, bellow are the new lines and then
the full buildspec.yml file
1# ...2env:3 secrets-manager:4 DEPLOY_TOKEN: secrets:DEPLOY_TOKEN5# ...6phases:7 # ...8 post_build:9 commands:10 # ...11 - echo Start deploy on `date`12 - kubectl config set-credentials [USER_NAME] --token=$DEPLOY_TOKEN13 - kubectl config set-cluster [CLUSTER_NAME] --server=[CLUSTER_URL] --insecure-skip-tls-verify=true14 - kubectl config set-context [CONTEXT_NAME] --cluster=[CLUSTER_NAME] --user=[USER_NAME] --namespace [NAMESPACE]15 - kubectl config use-context [CONTEXT_NAME]16 - kubectl rollout restart deployment [DEPLOYMENT_NAME]17 - echo Deployment ready on `date`
NOTE: All variables between [] needs to be replaced with the right values, also depending on your needs you might want to store those values in secret manager.
The env section of the yaml is used to read and access the environment variables from the
buildspec.yml, each secret can store more than one value in order to a variable from a given secret
you need to declare that variable under env.secrets-manager section
Finally the full buildspec.yml
1version: 0.223env:4 secrets-manager:5 DEPLOY_TOKEN: secrets:DEPLOY_TOKEN67phases:8 pre_build:9 commands:10 - echo Logging in to Amazon ECR...11 - aws ecr get-login-password --region $AWS_DEFAULT_REGION | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin $AWS_ACCOUNT_ID.dkr.ecr.$AWS_DEFAULT_REGION.amazonaws.com12 - echo Generating tag...13 - COMMIT_HASH=$(echo $CODEBUILD_RESOLVED_SOURCE_VERSION | cut -c 1-7)14 - IMAGE_TAG=${COMMIT_HASH:=latest}15 build:16 commands:17 - echo Build started on `date`18 - echo Building the Docker image...19 - docker build -t $IMAGE_REPO_NAME:$IMAGE_TAG . -f Dockerfile20 - docker tag $IMAGE_REPO_NAME:$IMAGE_TAG $AWS_ACCOUNT_ID.dkr.ecr.$AWS_DEFAULT_REGION.amazonaws.com/$IMAGE_REPO_NAME:$IMAGE_TAG21 - docker tag $IMAGE_REPO_NAME:$IMAGE_TAG $AWS_ACCOUNT_ID.dkr.ecr.$AWS_DEFAULT_REGION.amazonaws.com/$IMAGE_REPO_NAME:$DEPLOY_TAG22 post_build:23 commands:24 - echo Build completed on `date`25 - echo Pushing the Docker image...26 - docker push $AWS_ACCOUNT_ID.dkr.ecr.$AWS_DEFAULT_REGION.amazonaws.com/$IMAGE_REPO_NAME:$IMAGE_TAG27 - docker push $AWS_ACCOUNT_ID.dkr.ecr.$AWS_DEFAULT_REGION.amazonaws.com/$IMAGE_REPO_NAME:$DEPLOY_TAG28 - echo Start deploy on `date`29 - kubectl config set-credentials [USER_NAME] --token=$DEPLOY_TOKEN30 - kubectl config set-cluster [CLUSTER_NAME] --server=[CLUSTER_URL] --insecure-skip-tls-verify=true31 - kubectl config set-context [CONTEXT_NAME] --cluster=[CLUSTER_NAME] --user=[USER_NAME] --namespace [NAMESPACE]32 - kubectl config use-context [CONTEXT_NAME]33 - kubectl rollout restart deployment [DEPLOYMENT_NAME]34 - echo Deployment ready on `date`